Genómica y Proteómica
Guía de trabajos prácticos de la materia
Guía de TPs Guía de comandos básicos de Linux
Licenciaturas en Biotecnología y en Bioinformática - FAIN - UADE

Guía de trabajos prácticos de la materia
Guía de TPs Guía de comandos básicos de Linux
Licenciaturas en Biotecnología y en Bioinformática - FAIN - UADE

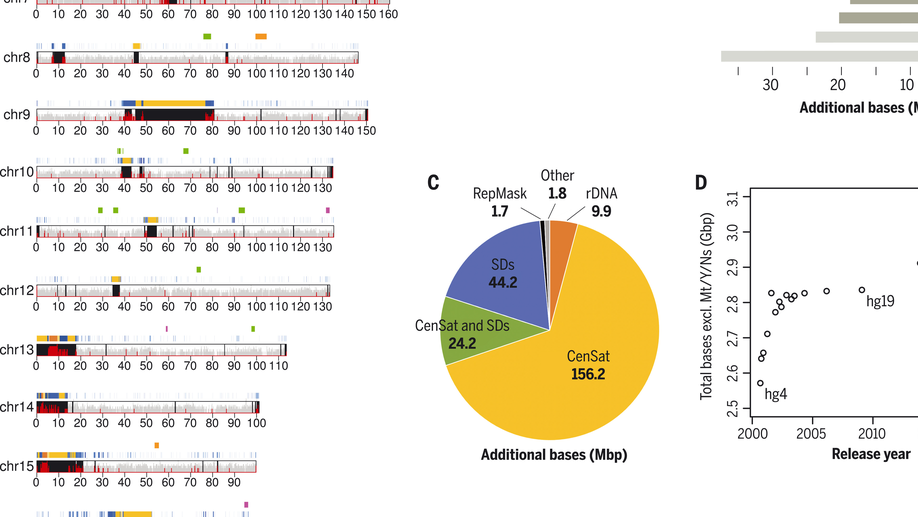
Sergey Nurk et al. ,The complete sequence of a human genome. Science376,44-53(2022). DOI:10.1126/science.abj6987
Since its initial release in 2000, the human reference genome has covered only the euchromatic fraction of the genome, leaving important heterochromatic regions unfinished. Addressing the remaining 8% of the genome, the Telomere-to-Telomere (T2T) Consortium presents a complete 3.055 billion–base pair sequence of a human genome, T2T-CHM13, that includes gapless assemblies for all chromosomes except Y, corrects errors in the prior references, and introduces nearly 200 million base pairs of sequence containing 1956 gene predictions, 99 of which are predicted to be protein coding. The completed regions include all centromeric satellite arrays, recent segmental duplications, and the short arms of all five acrocentric chromosomes, unlocking these complex regions of the genome to variational and functional studies.
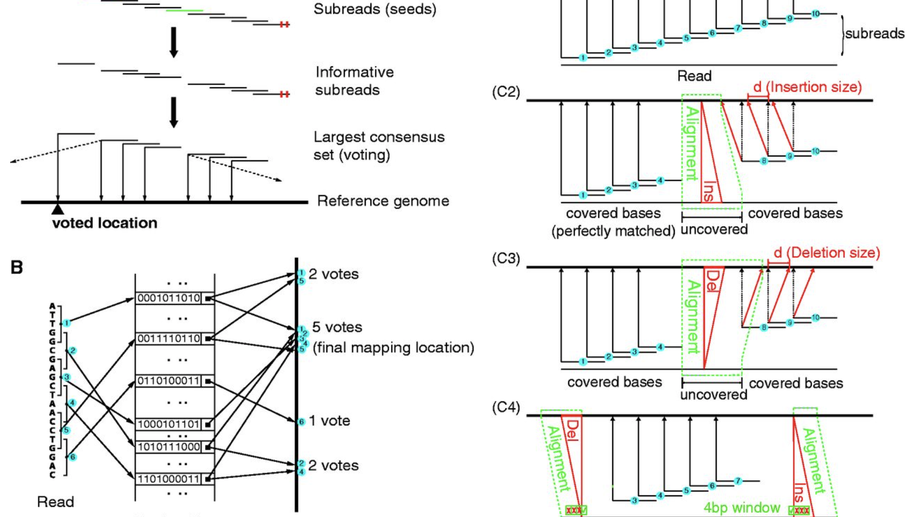
Yang Liao, Gordon K. Smyth, Wei Shi, The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 41, Issue 10, 1 May 2013, Page e108, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt214
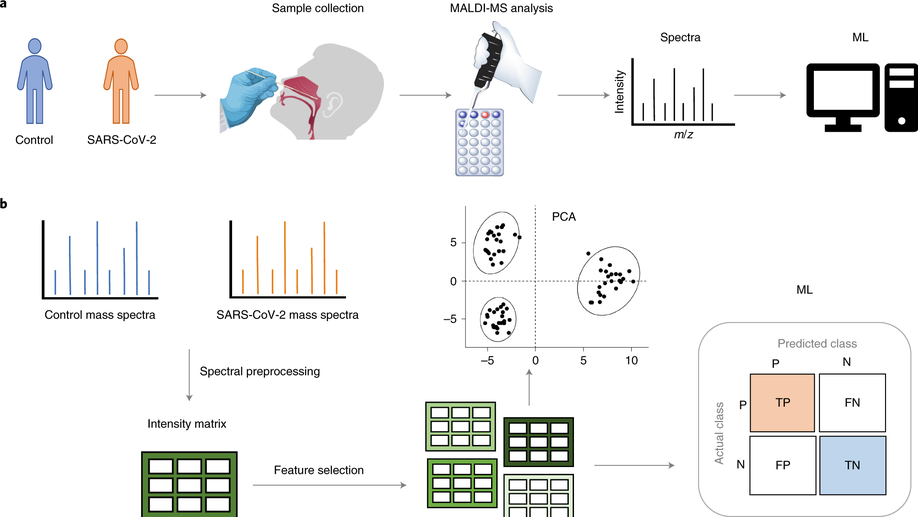
Nachtigall, F.M., Pereira, A., Trofymchuk, O.S. et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swabs using MALDI-MS. Nat Biotechnol (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0644-7
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 using RT–PCR and other advanced methods can achieve high accuracy. However, their application is limited in countries that lack sufficient resources to handle large-scale testing during the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, we describe a method to detect SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swabs using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) and machine learning analysis. This approach uses equipment and expertise commonly found in clinical laboratories in developing countries. We obtained mass spectra from a total of 362 samples (211 SARS-CoV-2-positive and 151 negative by RT–PCR) without prior sample preparation from three different laboratories. We tested two feature selection methods and six machine learning approaches to identify the top performing analysis approaches and determine the accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 detection. The support vector machine model provided the highest accuracy (93.9%), with 7% false positives and 5% false negatives. Our results suggest that MALDI-MS and machine learning analysis can be used to reliably detect SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swab samples.
| Clase | Fecha | Temas | Docente | Auxiliar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5/8 | Introducción | JB | CC |
| 2 | 12/8 | Genómica I | JB | CC |
| 3 | 19/8 | Genómica II | JB | CC |
| 4 | 26/8 | TP1: Análisis de variantes genómicas | JB | CC |
| 5 | 2/9 | Genómica III y Seminario | YM | CC |
| 6 | 9/9 | TP2: Bases de datos genómicas | JB | CC |
| 7 | 16/9 | Transcriptómica I | YM | CC |
| 8 | 23/9 | Transcriptómica II | YM | |
| 9 | 30/9 | Repaso + ejercitación | JB | |
| 10 | 7/10 | TP3/4/5: Análisis transcriptómico | YM | CC |
| 11 | 14/10 | TP3/4/5: Análisis transcriptómico | YM | CC |
| 12 | 21/10 | Parcial | YM | CC |
| 13 | 28/10 | Proteómica I | JB | CC |
| 14 | 4/11 | Speakers invitados | JB | CC |
| 15 | 11/11 | TP6: Análisis de datos de proteómica | JB | CC |
| 16 | 18/11 | Feriado | ||
| 17 | 25/11 | Journal Club | JB | CC |
| 18 | 2/12 | Recuperatorio y final adelantado | JB | CC |
| EXAMEN FINAL | 16/12 | Final regular | JB | CC |
Clase adicional sábado: 2/11 - Clase virtual por Teams - 9 a 13 hs. - Proteómica II - JB
| Class | Date | Topics | Professor | Assistant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5/8 | Introduction | JM | |
| 2 | 12/8 | Genomics I | YM | |
| 3 | 19/8 | Genomics II | YM | |
| 4 | 26/8 | Lab Session 1: Genomic Variant Analysis | YM | |
| 5 | 2/9 | Genomics III & Seminar | YM | |
| 6 | 9/9 | Lab Session 2: Genomic Databases | YM | |
| 7 | 16/9 | Transcriptomics I | JM | |
| 8 | 23/9 | Lab Session 3/4/5: Transcriptomic Analysis | JM | CC |
| 9 | 30/9 | Lab Session 3/4/5: Transcriptomic Analysis | JM | CC |
| 10 | 7/10 | Recap | JM | |
| 11 | 14/10 | Mid-Term Exam | JM | |
| 12 | 21/10 | Proteomics I | JM | |
| 13 | 28/10 | Proteomics II | JM | |
| 14 | 4/11 | Guest Speakers | JM | |
| 15 | 11/11 | Lab Session 6: Proteomic Data Analysis | YM | |
| 16 | 18/11 | No Class | ||
| 17 | 25/11 | Journal Club | JM | |
| 18 | 2/12 | Remedial Exam and Early Final | JM | |
| FINAL EXAM | 16/12 | Regular Final Exam | JM |
Saturday extra class: 21/9 - Virtual class by Teams - 9 to 13 hs. - Transcriptomics II - JM
*La presente guía de trabajos prácticos de Genómica y Proteómica 2024 fue confeccionada por Romina Girotti, Yamil Mahmoud y Juan Bizzotto. El contenido de la guía está organizado para ser utilizado en el contexto de la materia, en conjunto con las clases teóricas dictadas por el equipo docente. Cada uno de los trabajos prácticos cuenta con un protocolo y su bibliografía correspondiente. Las actividades a desarrollar en la presente edición de la materia fueron diseñadas por Romina Girotti (TP2 y TP6), Yamil Mahmoud (TP1, TP3, TP4 y TP5), Juan Bizzotto (TP2 y TP6), Federico Prada (TP5) y Andrea Llera (TP5, TP6). El desarrollo de la máquina virtual estuvo a cargo de Yamil Mahmoud.